Maximum Stock Price A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Maximum Stock Price
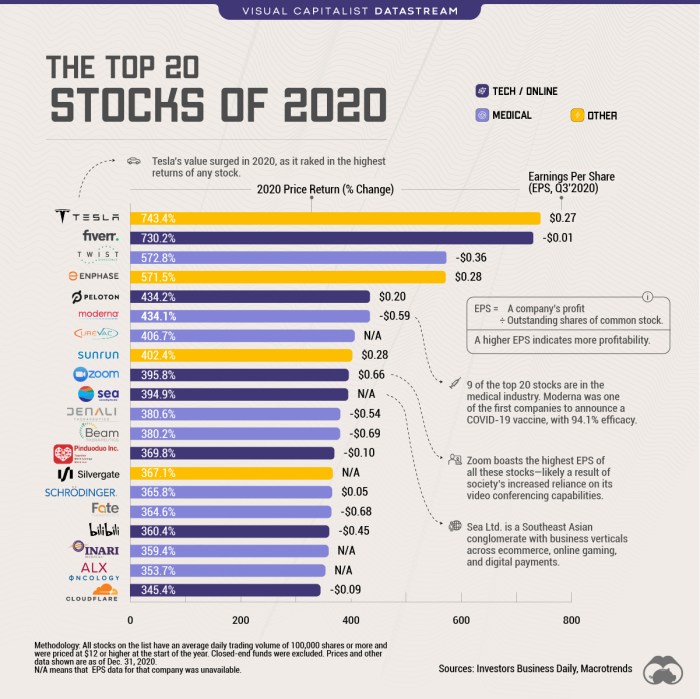
Source: visualcapitalist.com
The maximum stock price, representing the highest price a stock has ever traded at, offers valuable insights into a company’s historical performance and market perception. Understanding this peak price requires examining its determinants, accessing reliable data, and considering its implications within broader market contexts and company-specific factors. This exploration will delve into the definition, identification, market influences, company performance correlations, prediction challenges, and overall significance of a stock’s maximum price.
Defining “Maximum Stock Price”
A stock’s maximum historical price is the absolute highest price at which a single share of that company’s stock has ever traded on a given exchange. This isn’t simply the highest price on a particular day or week; it represents the all-time peak across the entire trading history of the stock. Several factors contribute to reaching this peak, including strong financial performance, positive market sentiment, industry trends, and macroeconomic conditions.
Determining a maximum stock price is inherently complex, influenced by various market factors and company performance. Understanding historical trends is crucial, and for LXP, a helpful resource for this is the detailed information available at lxp stock price tracking website. Ultimately, projecting a maximum price requires careful consideration of both internal and external pressures influencing the market.
Companies like Apple (AAPL) and Microsoft (MSFT) serve as prime examples, having reached exceptionally high maximum stock prices due to their sustained growth and dominance in their respective sectors. The maximum stock price is distinct from other price points such as the all-time high (which may reset after a period of time), and the 52-week high (the highest price within the past year).
While all-time high and 52-week high represent significant milestones, the maximum stock price provides a long-term perspective on a company’s valuation.
Identifying Maximum Stock Price Data
Obtaining accurate historical stock price data requires utilizing reliable financial data providers. Several resources offer comprehensive historical stock information, including dedicated financial websites, brokerage platforms, and specialized data vendors. These resources typically provide detailed historical price charts, allowing users to identify the maximum stock price. Cross-referencing data from multiple sources helps verify accuracy and identify potential discrepancies. Reliable financial data providers include reputable sources like Yahoo Finance, Google Finance, Bloomberg, Refinitiv, and FactSet.
A robust process for verifying data involves comparing the maximum stock price across multiple sources, checking for inconsistencies, and considering potential data lags or errors.
Maximum Stock Price and Market Conditions
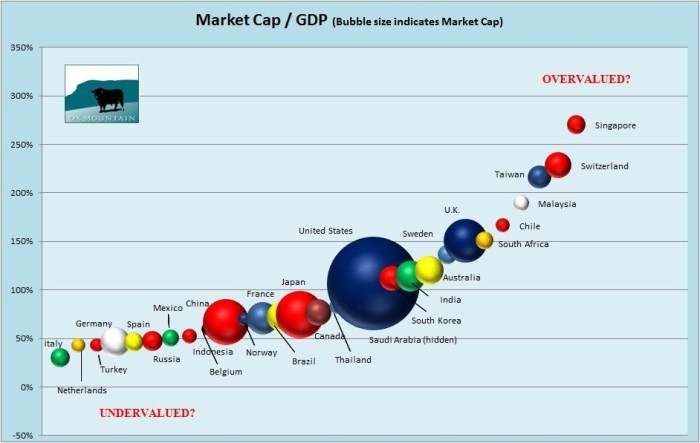
Source: monevator.com
A company’s maximum stock price is heavily influenced by prevailing market conditions. Economic booms often correlate with increased investor confidence, leading to higher stock valuations. Conversely, recessions can significantly depress stock prices, even for fundamentally strong companies. Market events, such as technological breakthroughs, geopolitical shifts, or regulatory changes, can also dramatically impact a company’s maximum stock price. For example, the dot-com bubble of the late 1990s led to exceptionally high maximum stock prices for many technology companies, followed by a sharp correction.
The following table illustrates how maximum stock prices can vary across sectors during different economic periods.
| Company Name | Sector | Maximum Stock Price | Economic Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Company A | Technology | $150 | Economic Boom |
| Example Company B | Energy | $75 | Economic Recession |
| Example Company C | Healthcare | $120 | Economic Boom |
| Example Company D | Finance | $50 | Economic Recession |
Maximum Stock Price and Company Performance

Source: depositphotos.com
A company’s financial performance is intrinsically linked to its maximum stock price. Strong earnings, revenue growth, and increasing market share often contribute to higher stock valuations. Conversely, negative news, such as declining profits, product recalls, or legal issues, can lead to price drops. Key financial metrics such as earnings per share (EPS), revenue growth, and return on equity (ROE) correlate with a stock reaching its maximum price.
Specific company events often preceding a peak in stock price include successful product launches, strategic acquisitions, and positive announcements about future prospects.
- Successful product launch
- Strategic acquisition
- Positive earnings surprise
- Announcing a new, innovative technology
- Securing a major contract
Predicting Future Maximum Stock Prices
Predicting future maximum stock prices is inherently challenging due to the complex interplay of factors influencing stock prices. While no method guarantees accurate prediction, models incorporating fundamental and technical analysis are used. Fundamental analysis assesses a company’s intrinsic value based on its financial statements and market position, while technical analysis studies price charts and trading volume patterns to identify potential trends.
For example, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario: A promising biotech company, “InnovateRx,” is developing a groundbreaking new drug. Positive clinical trial results and strong market anticipation could lead to a significant increase in its stock price. However, regulatory hurdles, competition, or unexpected side effects could negatively impact the stock’s trajectory, hindering its potential to reach a predicted maximum price.
The actual maximum price would depend on the balance of these and other factors.
The Significance of Maximum Stock Price
Understanding a company’s maximum stock price is crucial for investors. This data provides historical context, helping assess the potential upside and downside of an investment. Investors might use this information to establish stop-loss orders, preventing significant losses. Comparing the maximum stock price with other valuation metrics, such as the price-to-earnings ratio (P/E), provides a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s valuation and its potential for future growth.
It’s important to remember that the maximum stock price is a historical data point; it doesn’t necessarily predict future performance. However, it offers valuable insights into the market’s perception of the company at its peak.
FAQ Section: Maximum Stock Price
What is the difference between maximum stock price and all-time high?
While often used interchangeably, the “maximum stock price” generally refers to the highest price ever recorded for a stock, even if that price was briefly reached and not sustained. “All-time high” similarly refers to the highest price but usually implies a period of sustained high valuation.
How can I find the maximum stock price for a specific company?
Most reputable financial websites (e.g., Yahoo Finance, Google Finance) provide historical stock data, including the all-time high. You can also use dedicated financial data providers like Bloomberg or Refinitiv for more comprehensive information.
Does a high maximum stock price guarantee future success?
Absolutely not. Past performance is not indicative of future results. A high maximum stock price simply reflects a past point of high valuation; it doesn’t predict future growth or stability.
What are some common reasons for a stock price to drop significantly after reaching its maximum?
Several factors can cause a drop after a maximum: negative news (e.g., poor earnings reports, lawsuits), changing market conditions (e.g., economic recession), increased competition, or a correction after a period of rapid growth.